PS(Java)/인프런 강의 문제
[PS] 인프런 강의 - Graph 4. 그래프 최단거리(BFS)
UL :)
2022. 9. 26. 23:02
문제
다음 그래프에서 1번 정점에서 각 정점으로 가는 최소 이동 간선수를 출력하세요.
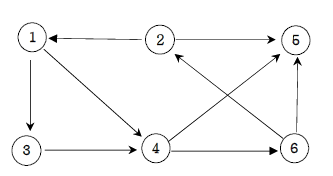
▣ 입력설명
첫째 줄에는 정점의 수 N(1<=N<=20)와 간선의 수 M가 주어진다. 그 다음부터 M줄에 걸쳐 연결정보가 주어진다.
▣ 출력설명
1번 정점에서 각 정점으로 가는 최소 간선수를 2번 정점부터 차례대로 출력하세요.
▣ 입력예제 1
6 9
1 3
1 4
2 1
2 5
3 4
4 5
4 6
6 2
6 5
▣ 출력예제 1
2 : 3
3 : 1
4 : 1
5 : 2
6 : 2
풀이
최단거리니까 BFS로 푼다. (그래서 큐를 사용한다)
앞서 문제들과 마찬가지로 방문기록을 남기기 위한 ch 배열이 필요한데,
이번에는 최소 이동 간선수 즉 레벨을 기록해두기 위한 배열 dis도 필요하다. (순서대로 출력하기 위함도 있고, 두번째 방법대로 풀기 위해서)
정점 v가 갈 수 있는 정점
정점 1: 3, 4 --> 여기서 dis[3],[4] 에 3, 4로의 최소 이동 간선수 = 레벨 1을 기록하고, ch[3], ch[4] = 1 로 방문기록
정점 2: 1, 5
정점 3: 4
정점 4: 5, 6
정점 5:
정점 6: 2, 5

코드
1. BFS 정석대로 (레벨로) 푸는 방법
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int n, m;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph; //integer를 저장할 수 있는 ArrayList를 저장하는 ArrayList
static int[] ch, dis; //방문 기록, 레벨 기록
//1번 정점에서 각 정점으로 가는 최소 이동 간선수
public static void BFS(int v) {
Queue<Integer> Q = new LinkedList<>();
Q.offer(v); //0레벨 루트
int L = 0; //레벨
while(!Q.isEmpty()) {
int len = Q.size();
//큐 순회
for(int i=0; i<len; i++) {
int cv = Q.poll(); //꺼냄
//x 정점이 갈 수 있는 정점 순회
for(int nv : graph.get(cv)) {
if(cv[nv] == 0) { //방문한 적이 없으면
ch[nv] = 1; //방문 기록
dis[nv] = L+1; //레벨 기록
Q.offer(nv); //큐에 추가
}
}
}
L++; //큐 순회가 끝나면 레벨 증가
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
n = in.nextInt(); //정점 개수
m = in.nextInt(); //간선 개수
ch = new int[n+1]; //2~n
dis = new int[n+1]; //2~n
graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
//정점 개수만큼 리스트 추가
for(int i=0; i<=n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
//단방향 그래프
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
int a = in.nextInt();
int b = in.nextInt();
graph.get(a).add(b);
}
ch[1] = 1;
BFS(1);
for(int i=2; i<=n; i++) {
System.out.println( i + " : " + dis[i]);
}
}
}
2. 강사님이 풀어주신 방법~ dis[nv] = dis[cv] + 1;
핵심코드 : dis[nv] = dis[cv] + 1; //cv의 레벨 +1
이차원 배열을 이용한 토마토 문제?를 풀기 위해서 이 방법을 알고 있어야 한다고 하심...
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int n, m;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph; //integer를 저장할 수 있는 ArrayList를 저장하는 ArrayList
static int[] ch, dis; //방문 기록, 레벨 기록
//1번 정점에서 각 정점으로 가는 최소 이동 간선수
public static void BFS(int v) {
Queue<Integer> Q = new LinkedList<>();
ch[v] = 1;
dis[v] = 0;
Q.offer(v);
while(!Q.isEmpty()) {
int cv = Q.poll(); //큐에서 꺼낸 정점: cv
//cv가 갈 수 있는 정점 순회
for(int nv : graph.get(cv)) {
if(ch[nv] == 0) {
ch[nv] = 1;
dis[nv] = dis[cv] + 1; //cv의 레벨 +1
Q.offer(nv);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
n = in.nextInt(); //정점 개수
m = in.nextInt(); //간선 개수
ch = new int[n+1]; //2~n
dis = new int[n+1]; //2~n
graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
//정점 개수만큼 리스트 추가
for(int i=0; i<=n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
//단방향 그래프
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
int a = in.nextInt();
int b = in.nextInt();
graph.get(a).add(b);
}
ch[1] = 1;
BFS(1);
for(int i=2; i<=n; i++) {
System.out.println( i + " : " + dis[i]);
}
}
}